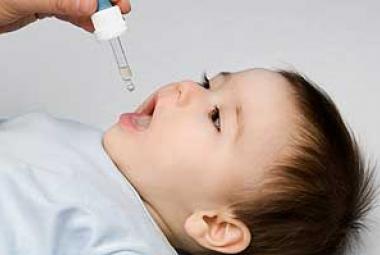
Oral Glucose Gel May be Effective Treatment for Neonatal Hypoglycemia
Neonatal hypoglycemia (low blood sugar in a new baby) is a common problem in hospital nurseries. Some infants can have low blood sugar and show no symptoms, others become jittery and may feed poorly, ...